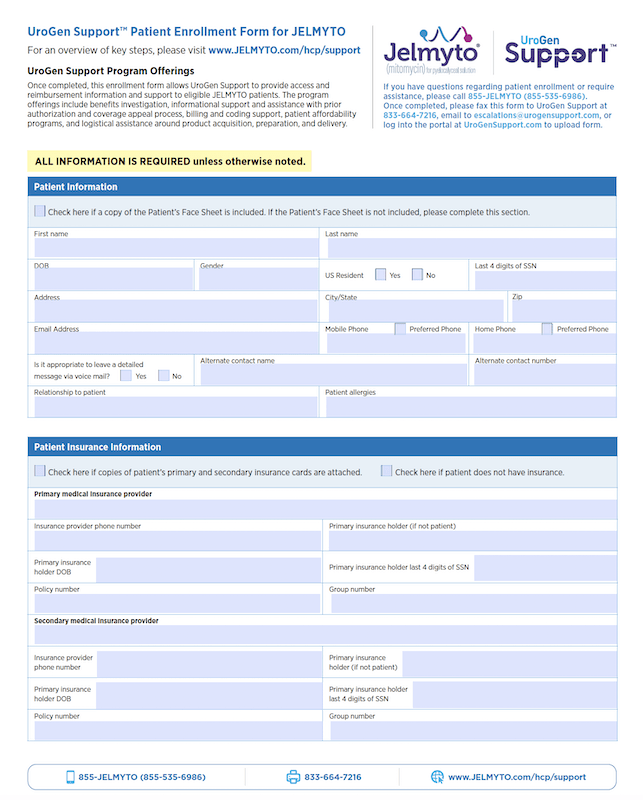
For patients with low-grade upper tract urothelial cancer
Endoscopic management is a good start, but it may not be enough1

Jim, 64
Newly diagnosed with multifocal disease

Sidney, 71
Recurrent, previously endoscopically managed with one resectable tumor
Jelmyto once weekly for 6 weeks for newly diagnosed or recurrent patients with low-grade UTUC2
Mitomycin for pyelocalyceal solution (JELMYTO) should NOT be instilled immediately following resection or ablation. Please refer to the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) and the AUA/SUO Guideline for principles of instillation therapy.3,4
Please click here for Olympus Study details.
Featured resources
Download these resources to learn more and to get your appropriate patients started on Jelmyto treatment.
Indications and Usage
Jelmyto® (mitomycin) for pyelocalyceal solution is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with low-grade Upper Tract Urothelial Cancer (LG-UTUC).
Important Safety Information
Contraindications
Jelmyto is contraindicated in patients with perforation of the bladder or upper urinary tract.
Ureteric Obstruction
Ureteric obstruction, including ureteral stenosis and hydronephrosis, occurred in patients receiving Jelmyto. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of ureteric obstruction, including flank pain, and fever, and for changes in renal function. Patients who experience obstruction may require transient or long-term ureteral stents or alternative procedures. Withhold or permanently discontinue JELMYTO based on the severity of ureteric obstruction.
Bone Marrow Suppression
The use of Jelmyto can result in bone marrow suppression, particularly thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. The following tests should be obtained prior to each treatment: Platelet count, white blood cell count differential and hemoglobin. Withhold JELMYTO for Grade 2 thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. Permanently discontinue for Grade 3 or greater thrombocytopenia or neutropenia.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, Jelmyto can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of mitomycin resulted in teratogenicity. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JELMYTO and for 6 months following the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JELMYTO and for 3 months following the last dose.
Common Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions in ≥ 20% of patients treated with Jelmyto were ureteric obstruction, flank pain, urinary tract infection, hematuria, abdominal pain, fatigue, renal dysfunction, nausea, dysuria, and vomiting.
Additional Adverse Reactions Information
Selected clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% and ≥ 2% of patients who received Jelmyto include urinary tract inflammation, bladder spasm, urosepsis, hypersensitivity, and instillation site pain.
Use in Specific Populations
Lactation
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Jelmyto and for 1 week following the last dose.
Preparation and Administration Information
Jelmyto is for pyelocalyceal use only and not for intravenous use, topical use, or oral administration. Jelmyto must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider. To ensure proper dosing, it is important to follow the preparation instructions found in the JELMYTO Instructions for Pharmacy and administration instructions found in the JELMYTO Instructions for Administration.
Jelmyto may discolor urine to a violet to blue color following the instillation procedure. Advise patients to avoid contact with urine for at least six hours post-instillation, to void urine sitting on a toilet, and to flush the toilet several times after use.
Jelmyto is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.
Please click here for Full Prescribing Information, Instructions for Pharmacy, and Instructions for Administration.
References: 1. Petros FG, Li R, Matin SF. Endoscopic approaches to upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am. 2018;45(2):267-286. 2. JELMYTO [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: UroGen Pharma, Inc.; 2022. 3. Coleman JA, Clark PE, Bixler BR, et al. Diagnosis and management of non-metastatic upper tract urothelial carcinoma: AUA/SUO guideline. J Urol. 2023;209(6):1071-1081. 4. Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Bladder Cancer V.3.2024. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2024. All rights reserved. Accessed April 16, 2024. To view the most recent and complete version of the guidelines, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.